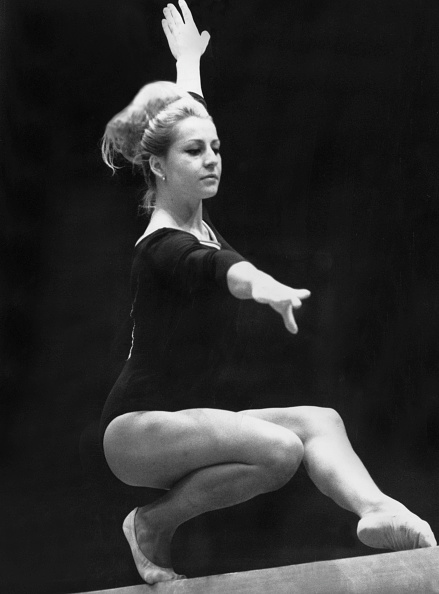
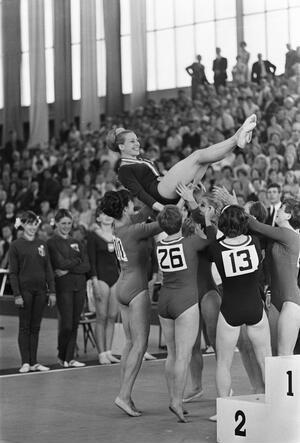Hana Růžičková didn’t want to be a gymnast. She dreamed of wearing white skating boots, but when those boots never materialized, she started gymnastics in 1956 at the age of fifteen. By 1960, she was a member of the Czechoslovak team that won silver at the Rome Olympics, and one year later, in 1961, Hana Růžičková was the surprise champion of the Czechoslovak Championships. (Věra Čáslavská fell off beam, and Růžičková was able to capitalize on it.)
What follows is a translation of a profile on Růžičková. It was printed in February of 1962, a few weeks after her win at the 1961 Czechoslovak Championships. Not only does it tell the story of a gymnast from a small village who had to balance work, training, and a long commute, but it also raises broader questions, such as: At what age should athletes start special training?
[Note: The age at which Růžičková started gymnastics sometimes varies in articles. For example, the report on the 1961 Championships suggested that she started in 1958.]